Laparoscopic Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch
 What is a Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch?
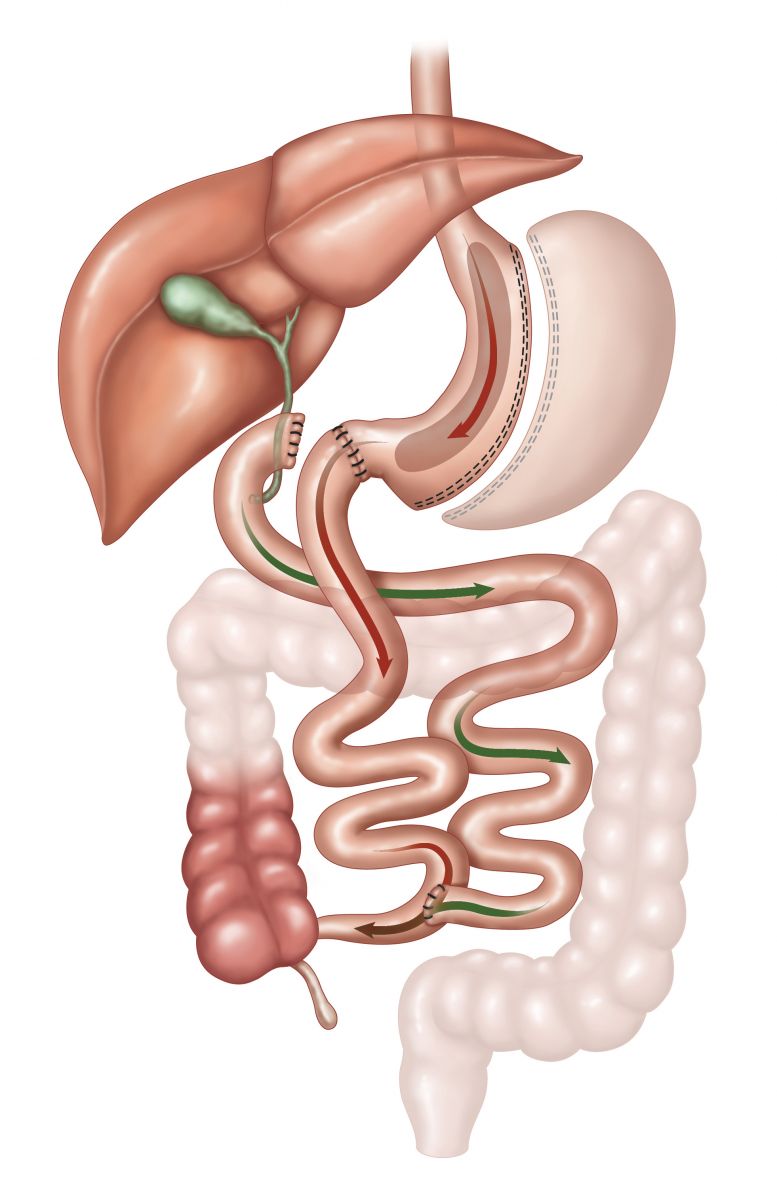
What is a Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch?
This biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch procedure results in decreased absorption of fat, calories and other nutrients which may result in increased weight-loss. Foods high in fat content are not easily absorbed and will be eliminated along with the usually high calories associated with the high-fat.
In all bariatric surgery procedures, carbohydrates and sugars are absorbed, so eating foods high in sugar (and calories) will still cause unwanted weight gain or difficulty to lose weight. Additionally, emphasis is placed on nutritionally beneficial and nutrient dense foods. The BPD/DS allows patients to increase portion size throughout, allowing for greater diversity in food consumption at each meal.
How is the Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch performed?
The outer margin of the stomach is removed (approximately two thirds—similar to a sleeve gastrectomy) and the intestines are then rearranged so that the area where the food mixes with the digestive juices is shortened.
A portion of the stomach is then left with the pylorus still attached and the duodenum beginning at its end. The duodenum is then divided, allowing for the pancreatic and bile drainage to be bypassed. This procedure preserves the pylorus, which eliminates “dumping syndrome” that can occur with gastric bypass.
